 |
v0.14.0 |
 |
v0.14.0 |
This tutorial shows how to create a simple 3D square mesh in Gmsh with some physical groups and then use the MoFEM tool read_med to generate a MoFEM-compatible input mesh for analysis. This would be largely the same as those presented in MSH-1: Create a 2D mesh from Gmsh which readers are recommended to have a look at first.
The steps presented in this turorial are as follows
read_med to generate a MoFEM-compatible input meshThe data presented in this tutorial can be found at the directory /mofem_install/mofem-cephas/mofem/users_modules/tutorials/msh-2
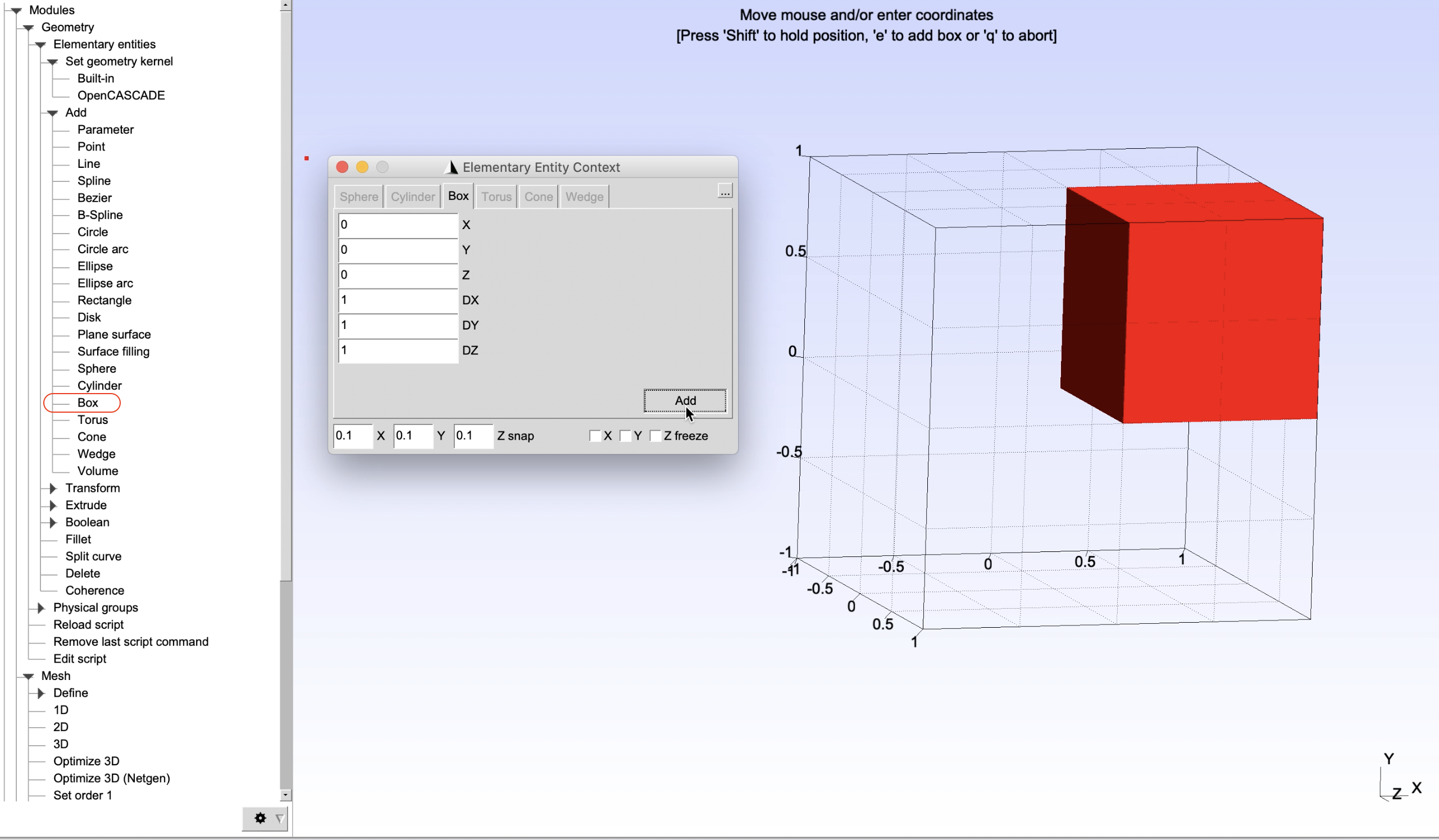
In order to create a geometry of a square, from the panel on the left, choose Modules -> Geometry -> Elementary entities -> Add -> Box. Then provide the geometry inputs including location (X, Y, Z) and dimensions (DX, DY, DZ) as shown in Figure 1 and click Add and then press q on the keyboard to finish.
As discussed in MSH-1: Create a 2D mesh from Gmsh, physical groups are used to define groups of entities that later will be given attributes which will be read by MoFEM during analysis.
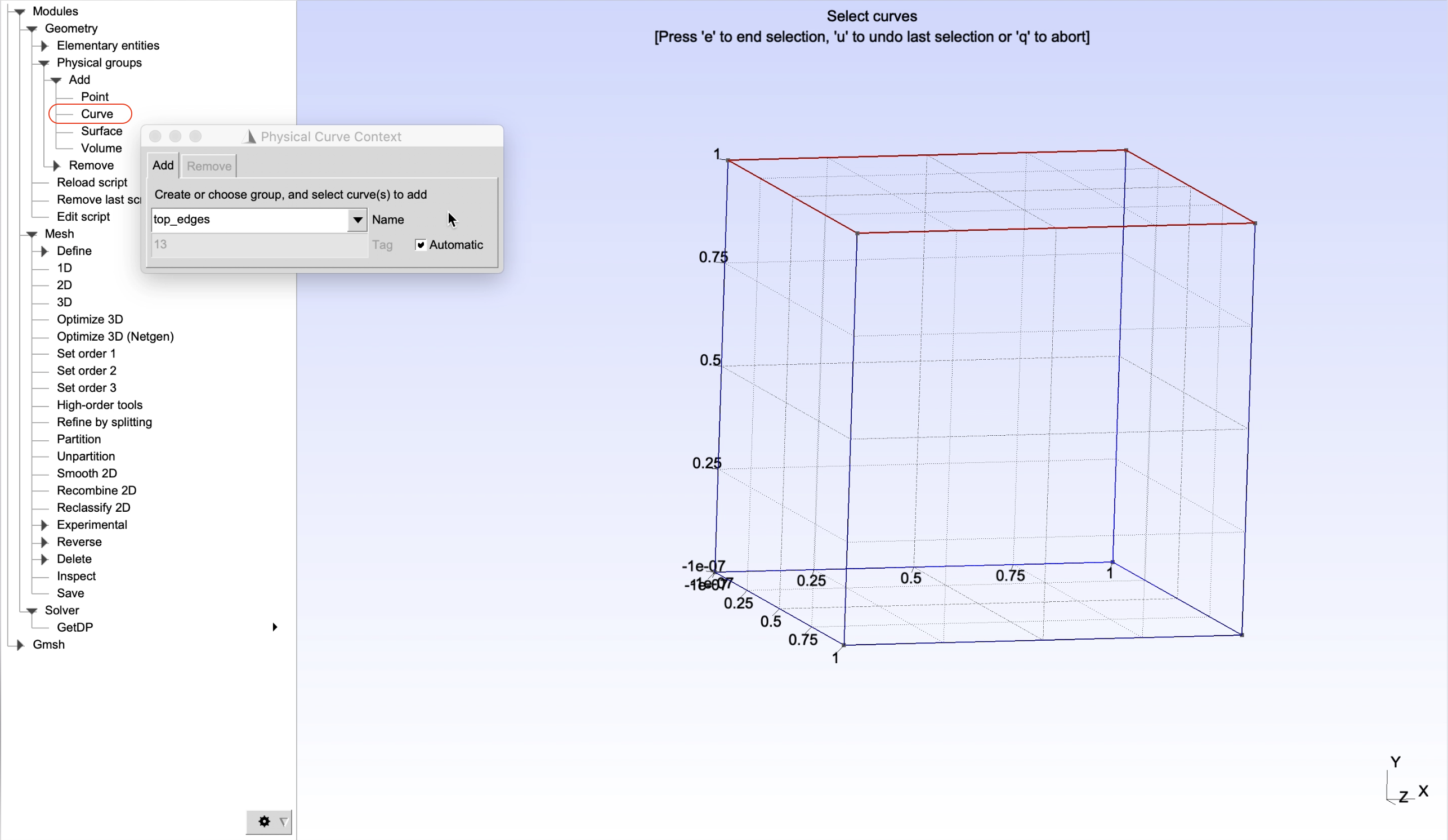
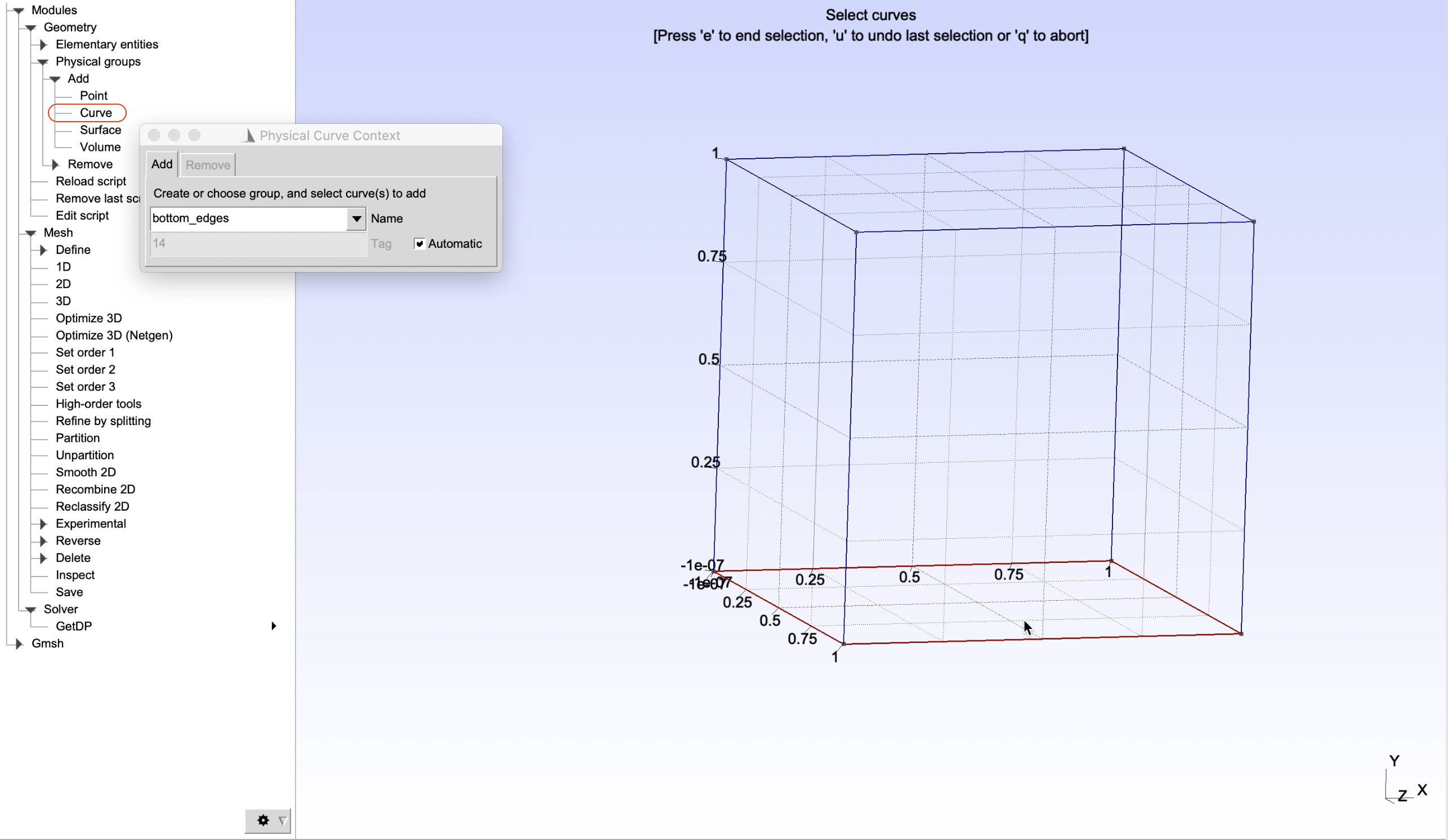
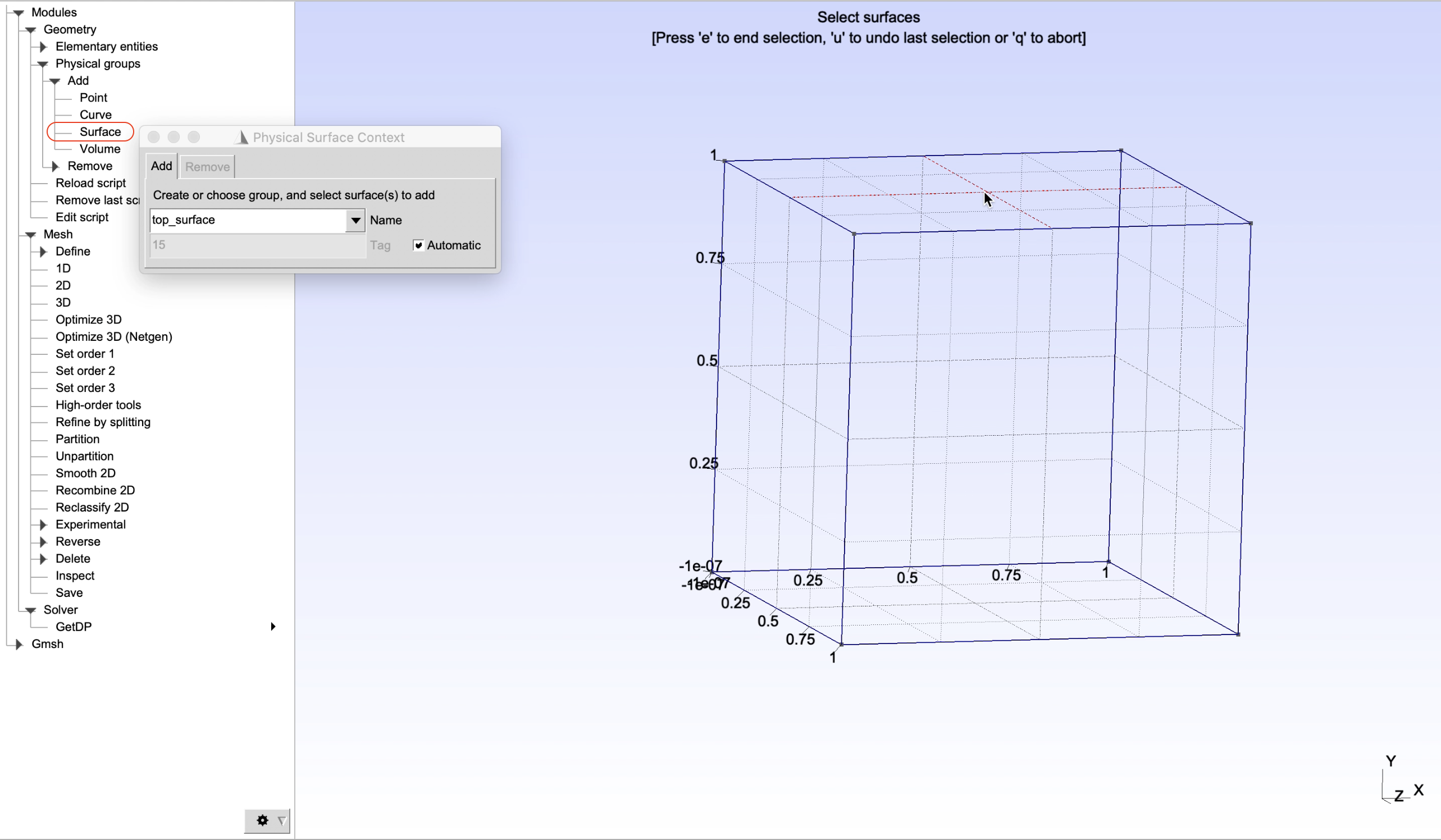
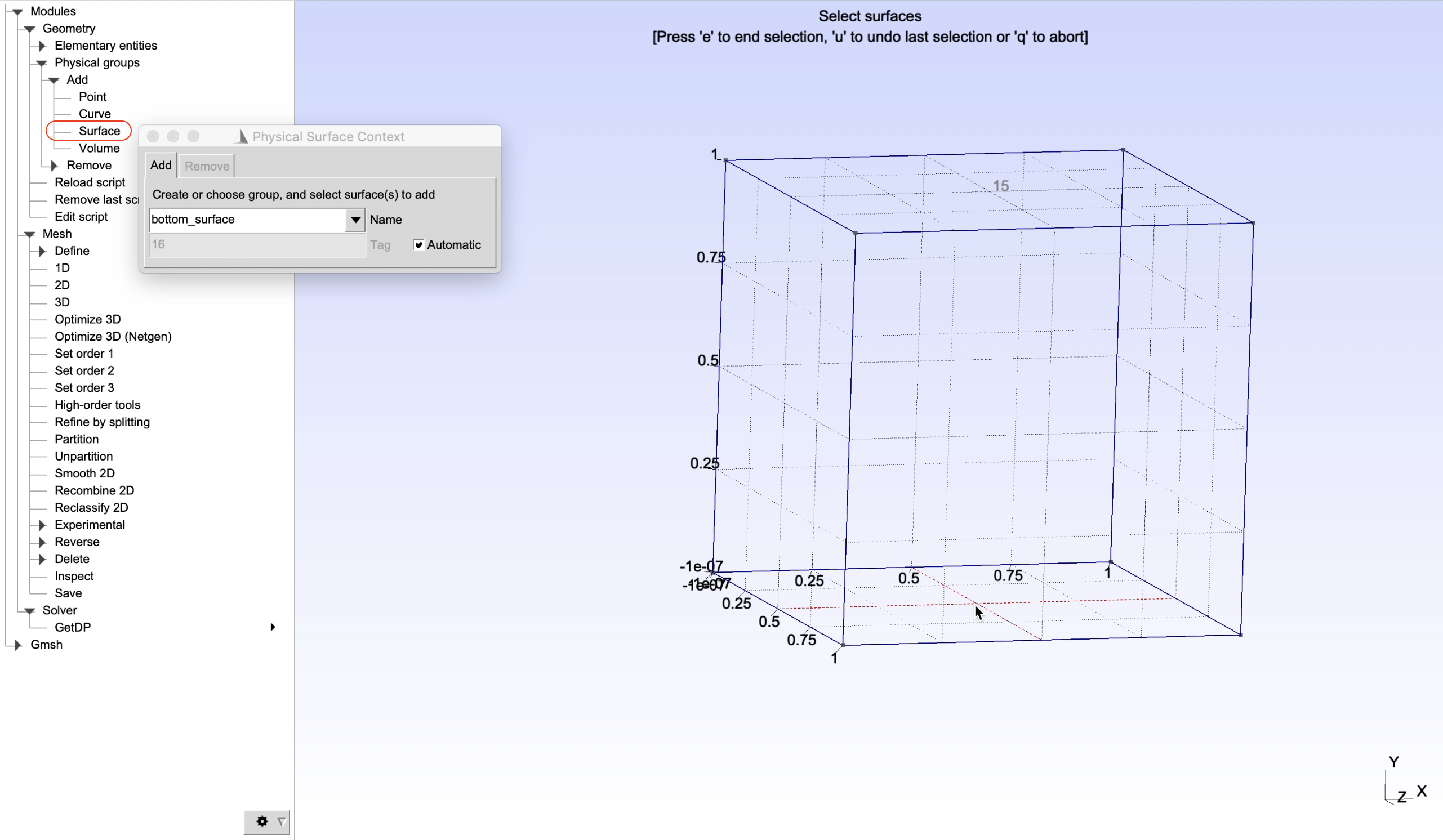
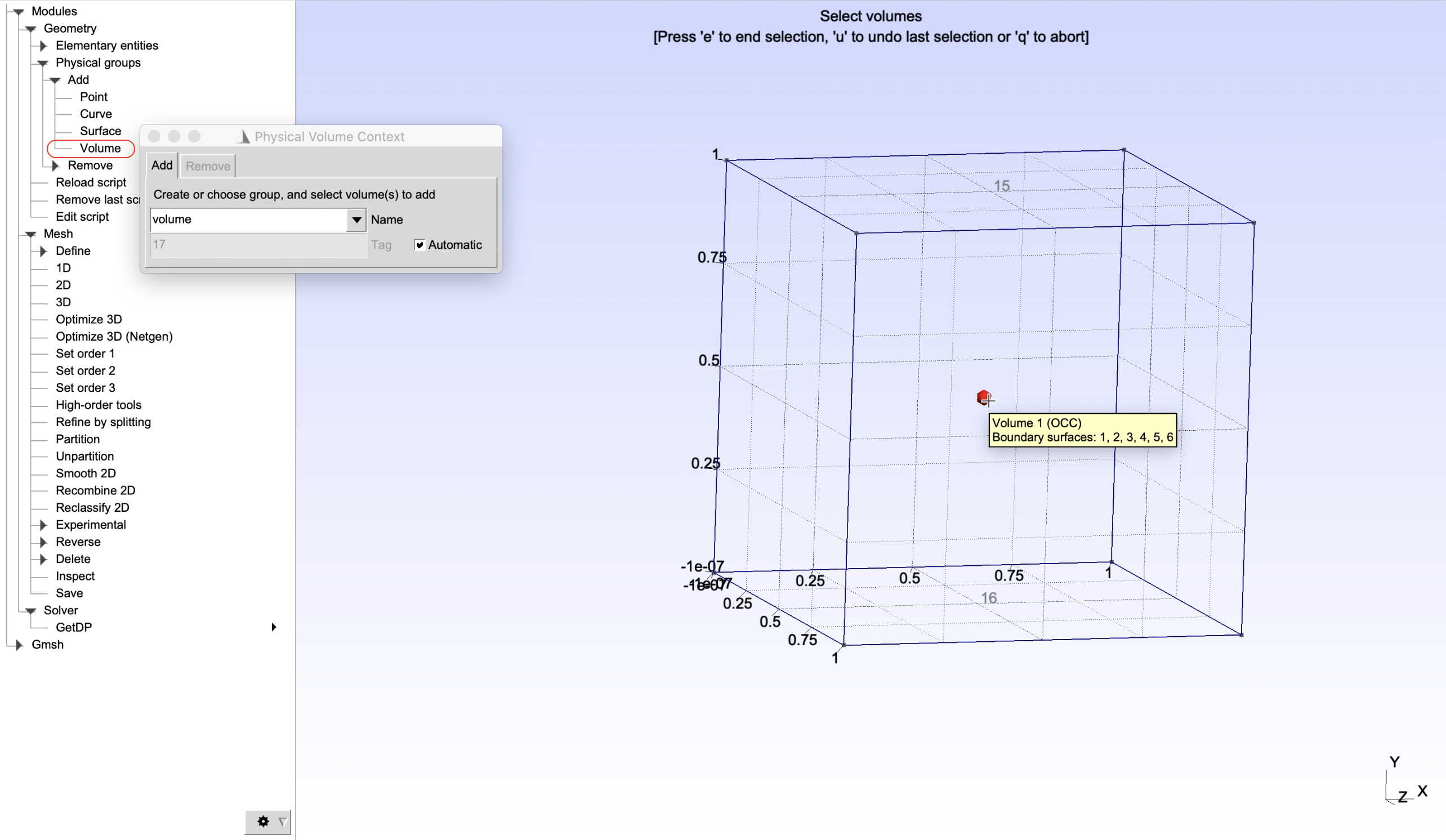
As a demonstration, physical groups of edges, surface and volume of the created cube will be defined as shown in Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, and Figure 6. It can be done by choosing, from the left panel, Modules -> Geometry -> Physical groups -> Add -> Curve/Surface/Volume. Then give name of a physical groups in the box Name, select entities to add to the corresponding groups and finally press e to end the selection.
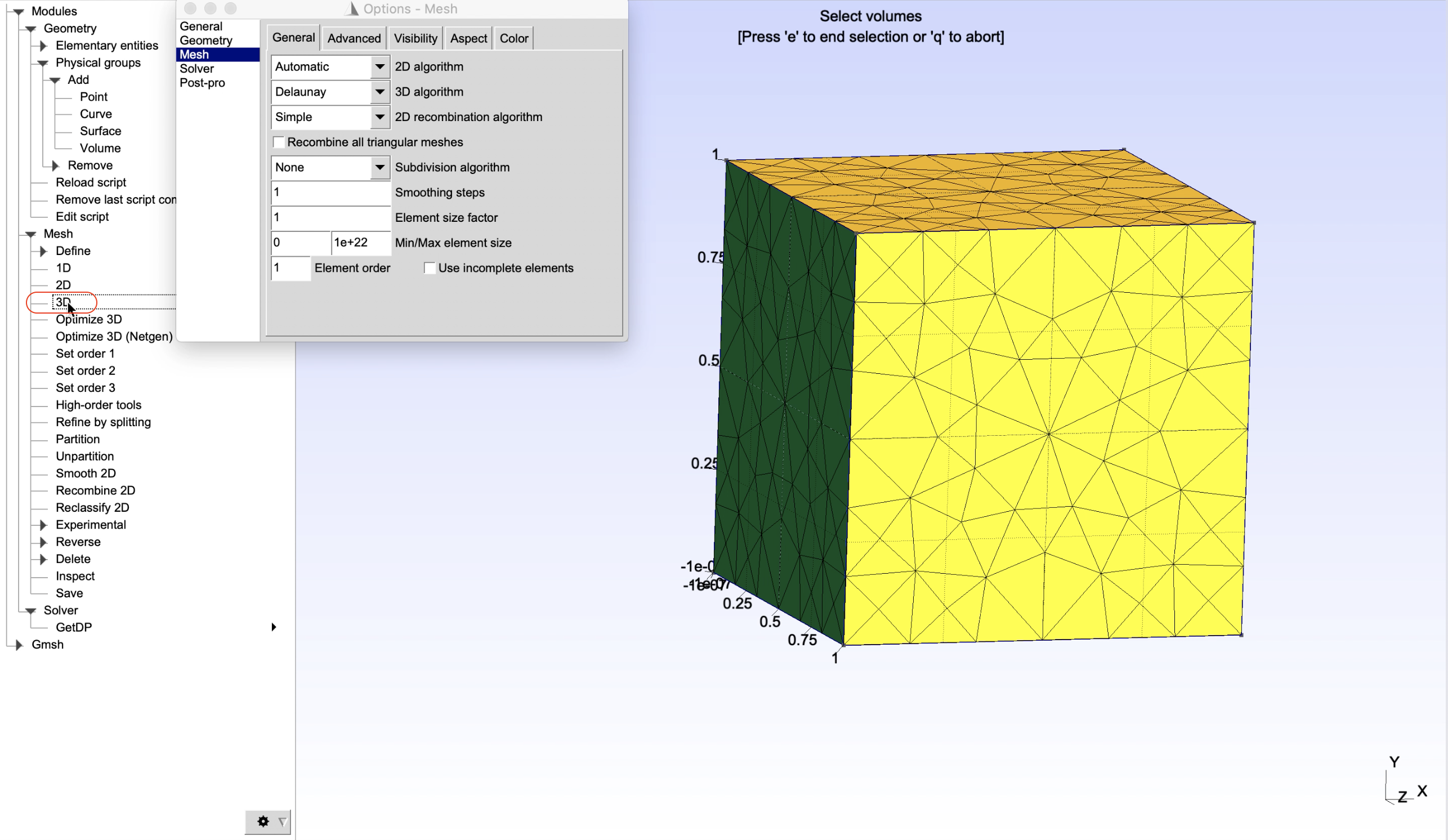
Go to Tools -> Options -> Mesh, in the General tab, choose the meshing algorithms and change the element size factor, e.g. 1 as shown in Figure 7, then close the window. To create the 2D mesh for the square, on the left panel, choose Modules -> Mesh -> 3D.
A preferred mesh format that will be exported is MED. This can be done by go to File -> Export ... then choose the file type Mesh - MED (*.med) and give a file name, e.g. cube.med
This section would be very similar to the one presented in MSH-1: Create a 2D mesh from Gmsh. The following steps will be presented
*.h5m format using read_med toolAs the mesh created by Gmsh does not contains attributes that may be needed for some tasks for analysis in MoFEM, e.g. blockset with a specific name to add material properties, boundary conditions, loadings. We need to know the exact ID of the physical group (blockset) in the MED file in order to add attributes to that blockset, we can check the IDs by running the read_med as follows
which would show that the defined physical groups along with their IDs as in the following output message
We would then use these IDs in the config file, named cube.config, as below to add materials properties (for block_1), add a specific name that can be used later in the source code to do certain operations (for block_2), directly add boundary conditions/constraints or springs (for block_3), and loading such as pressure (for block_5)
Once the MED file and config file are ready, the final mesh file in *.h5m format that contains necessary information and can read by MoFEM can be generated by running the command below
After running this command, the cube.h5m file will be created and the main part of the output message would look like this
As can be seen, along with the original blocksets 1 to 6, the output mesh cube.h5m now contains the three new blocksets 100, 110, 120 and 130 with additional attributes. Using the same concept, more blocksets for different purposes can be added to the mesh.
Once the final cube.h5m mesh is generated, it can be used directly as an input in MoFEM programs, e.g. elasticity or SCL-1: Poisson's equation (homogeneous BC).
